Archives
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-07
-
dnasei br Discussion br Acknowledgments Writing of this revi
2024-10-21
Discussion Acknowledgments Writing of this review and collection of data from our laboratories that are presented were supported by a grant from the Belgian Science Policy (BELSPO) SSTC Interuniversity Attraction Poles Plastoscine P7/17 to AVDL and JB, multiple grants from the Fund for Scienti
-
The studies have described that Candida non
2024-10-21
The studies have described that Candida non-albicans are considered as remarkable pathogenic agents of OPC, and among them, C. tropicalis and C. glabrata are known as major strains that may replace C. albicans as the greatest causing agent of this infection [20], [21]. It has been shown that Candida
-
gallic acid australia In conclusion we demonstrated that in
2024-10-21
In conclusion, we demonstrated that, in the skeletal muscle of rats with T1DM, CRBN levels increased and AMPK, Akt, GLUT4, PGC-1α, and FNDC5 levels decreased, resulting in increased fasting glucose levels. Aerobic exercise training decreased levels of CRBN, which was possibly mediated by AMPK, Akt,
-
AMPK is a central regulator of cell
2024-10-21

AMPK is a central regulator of cell growth, migration, metabolism, autophagy, and cell polarity [20], [21], [22], [23]. It is highly conserved in eukaryotes and functions as the primary sensor of intracellular adenosine nucleotides [24]. When intracellular ATP levels decrease, AMPK is activated to g
-
Introduction Lipoxygenases LOXs are key
2024-10-21
Introduction Lipoxygenases (LOXs) are key enzymes that catalyze the polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) such as arachidic BIRB796 (AA), linoleic acid (LA) and others unsaturated fatty acids (Brash, 1999). LOXs are expressed in immune, neural, epithelial, tumor cells and other cells (Claesson, 2009
-
However a high triglyceride level was associated with
2024-10-21
However, a high triglyceride level was associated with dementia in a study with subjects aged ≥65 years (Raffaitin et al., 2009). In another study, the serum triglyceride levels of three different transgenic mouse strains mimicking AD were also evaluated within the progression of the pathology. In o
-
In conclusion phenolic hydroxyl was introduced not only to
2024-10-21
In conclusion, phenolic hydroxyl was introduced not only to C3 side chain but also to C6 or C7 position of the quinoxalinone core, resulting in a new group of ARIs candidates exhibiting antioxidant activity. Biological activity tests suggested that compounds were not only sufficient to inhibit ALR2
-
AZD2858 receptor AMPK is an essential player in
2024-10-19
AMPK is an essential player in adiponectin signaling pathway that regulates energy metabolism. The fact that suppression of AMPK activity by compound C largely diminished candesartan-mediated inhibition of NFκB via blocking AT1 also suggests that the AT1-mediated effect is at least partly resulted f
-
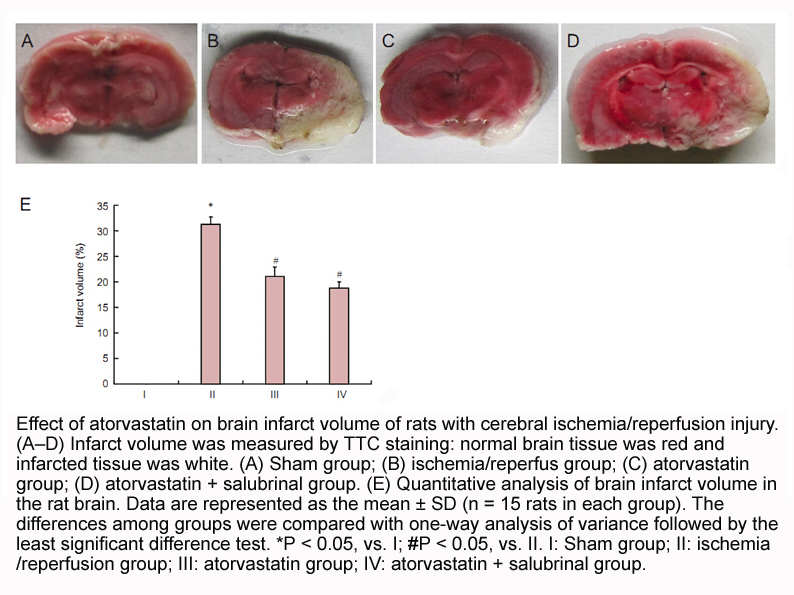
Fig A shows a schematic
2024-10-19
Fig. 2A shows a schematic representation of histological results according to the Franklin and Paxinos Mouse Brain Atlas (2001). The black circles represent the sites of drug infusion that were on-target within the amygdala. Gray circles represent the animals that had infusion locations outside the
-
ADORs accomplish a variety of physiological effects in diffe
2024-10-19
ADORs accomplish a variety of physiological effects in different tissues. In neurons, ADORs regulate the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and glutamate (Ferré et al., 1992; Fredholm and Dunwiddie, 1988; Ginsborg and Hirst, 1972; Gonçalves et al., 2015; Quarta et al., 2004; Stella et al.
-
JSH-23 br Experiment br Results and discussion
2024-10-19
Experiment Results and discussion Conclusion Introduction Tuberculosis (TB) is a chronic specific bacterial infection caused by bacteria of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis [1]. TB remains one of the deadliest diseases in the world. It is the second leading infectious cause of death after
-
br Results br Discussion The present study uncovers a
2024-10-19
Results Discussion The present study uncovers a role of calpain, a family of calcium-dependent protease, in regulating postsynaptic differentiation at the NMJ. Cholinergic activation stimulates calpain, whose inhibition stabilizes AChR clusters in cultured muscle Benzoquinonium dibromide and i
-
br ARIs in the prevention of prostate cancer Prostate
2024-10-19
5ARIs in the prevention of prostate cancer Prostate cancer continues to be a leading cause of male deaths worldwide. In 2009, it was estimated there would be 192,280 new cases of prostate cancer with a predicted 27,360 deaths [25]. Because androgens, and specifically DHT, play a large role in bot
-
In the previous study we
2024-10-19
In the previous study, we demonstrated the importance of the mPFC postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptor in the sustained antidepressant effects, because a sustained antidepressant effect was obtained with intra-mPFC injection, but not systemic injection of 8-OH-DPAT, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist (Fukumoto et al
-
Double immunofluorescence staining of Gas and
2024-10-19
Double immunofluorescence staining of Gas6 and Axl with neuronal specific nuclear protein (NeuN), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba-1), demonstrated that Gas6 and Axl are expressed by neurons, astrocytes and microglia/macrophages (Fig. 2). In
16097 records 77/1074 page Previous Next First page 上5页 7677787980 下5页 Last page